Decision Tree(DT) comes under Supervised Learning Model. It predicts either class or value based on past or historical data. DT can be used for classification and regression. Tree structure which has branches and nodes.
- Each branch connects nodes with “and”, and multiple branches connects by “or”.
##Two most popular Decision Tree Algorithm
C5.0
- In this algorithm we have multiple split
- We use Rule Based Pruning here ###CART
- In this algorithm we have Binary Split.
- We use Tree Based Pruning here.
Information Gain and Entropy
Information Gain (IG) = Entropy of the system before split - Entropy of the system after split.
Entropy = Uncertainty in the data or Measure of impurity
Can be calculated as below
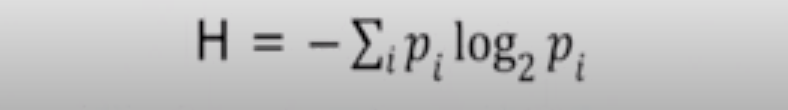
The basic rule here is, we select the node as parent whose information gain is high.
Now Let us see with an example.
Data set - Number of observation 70. We have four variables and those are below
- Number
- Age
- Gender
- Sensible
Independent Variables
In above, Number, Age , Gender are Independent Variables.
Dependent/Target Variable
Sensible is the Target Variable, which has yes or no values.
Training set
- First 50 observations considered as Training set, including 20 males and 30 females.
Test set
- Remaining 20 observations considered as Test set and we have only females in this data set.
Hypothesis
If man, then Sensible value is NO. If Woman, then Sensible Value is YES.
Steps to make a decision tree
- Identify a Parent Node.
- The variable with high information gain is considered as Parent Node.
- Calculate Information Gain for all the variables in the Dataset so that we can identify parent node.
- Once Parent Node is identified, we go for branches.
Calculation
IG = Entropy of system before split - Entropy after split
Entropy before split:
In Training set we have 50 observations, in which we are going to calculate Entropy before split.
- Number of Sensible People in 50 - 29
- Number of Insensible People in 50 - 21 ( Twenty males and one female)
Now Entropy before split is calculated below. 
Entropy After Split:
- Here the split is based on Gender
- We have 20 Males and 30 Females
- Entropy of the Male system = 20/20*log(20/20,2) = 0
- Entropy of the Female system = 29/30log(29/30,2)+1/30log(1/30,2) = 0.2108
- Entropy of Male after split + Entropy of Female after split
- 20/50(Male System) + 30/50(Female System)
- 3/5*02108 = 0.1265
- Information Gain = Entropy before split - after split
- 0.9814-0.1265= 0.8549
- Like this we have to calculate Information Gain for every variables in the data set.
- The variable with high Information Gain is considered as Parent Node,
Rules to Apply during Prediction
- Support
Frequency of the item in the dataset. Ex: If Male then credit card bill is high. Then it happens for most of the cases. So the support is high for credit card bill(high) for Male. - Confidence It is an indication that how often the rule is found to be true.. Ex: we predict that If Male, the cc bill is high. If that is true for many cases, then the confidence level is high..
- Lift Ratio of observed support.
We can understand this will solve some problem in practial. With this we close this page. Next page is obviously R Implementation with Decision Tree.