This page is all about Sampling Techniques.
What is Sampling
A Subset from an entire population
Why Sampling
When we are not able to analyse the entire population we choose sampling method
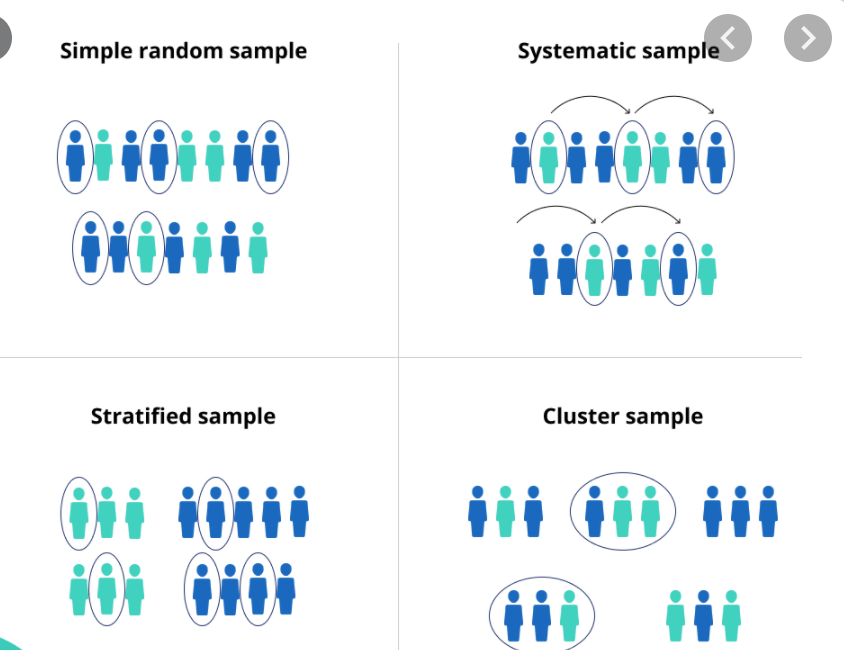
Types of Sampling
- Probability Samples
- Non Probability Samples
Probability Samples
- Simple Random
- Systematic Random
- Stratified
- Multi Stage Cluster
Non Probability Samples
- Convenience
- Snowball
- Quota
- Theoretical
- Self Selection
- Purposive
- Voluntary Response Lets see some of the sampling methods here..
Simple Random Sampling
In this sampling, every single observation has an equal chance of being selected. In this sampling, we create a column with random value for every single observation. Then we randomly pick the numbers assigned, which means the observation assigned to that number has been picked up.
We can use R to generate the random numbers or we can directly take from the columns. See the picture below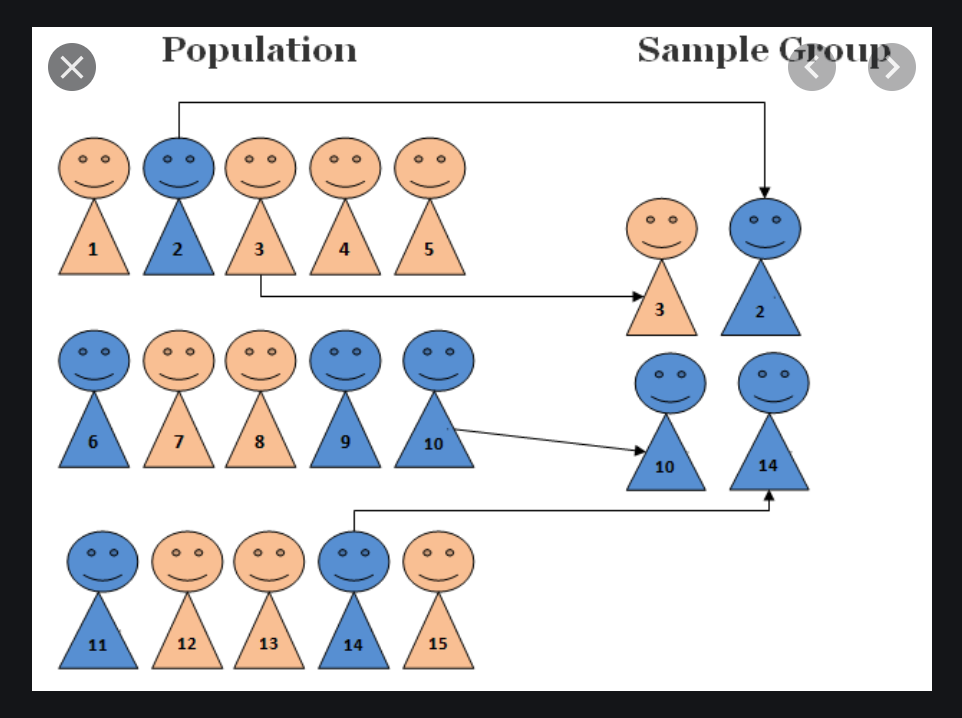
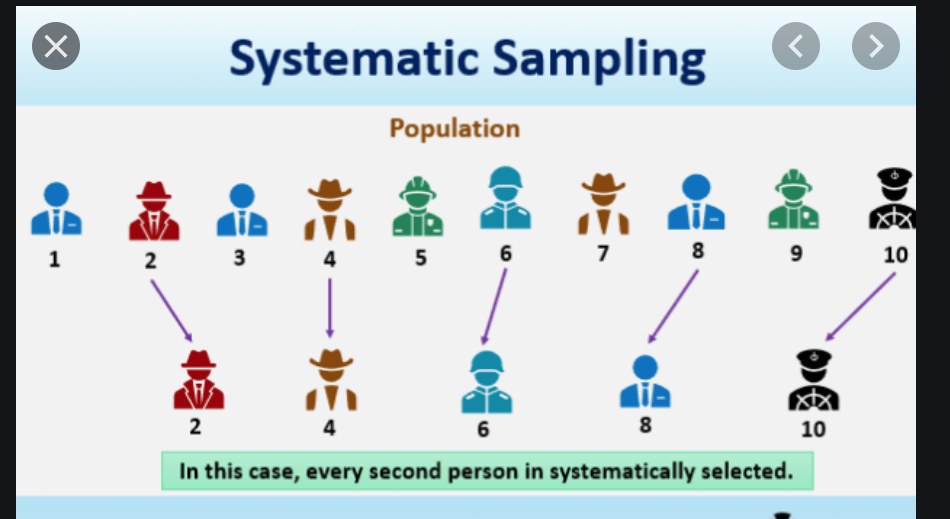
Systematic sampling
It is also called as Kth Name selection technique.
K = N/n
N = Number of observations ;
n = Desired Sample
After we calculate K, every Kth number is selected from the list of population.
We need to ensure there is no hidden records in the dataset for this sampling. See below for better understanding
Stratified sampling
We go for this sampling when we find low relation between sub groups. In this sampling the population is divided into stratum. Stratum is a subset here.
- Identify a categorical variable which is more related to the Target variable. ( Target variable is nothing but a variable on which you would like to build your analysis or deeper understanding) .
- we need to apply the stratified sampling technique, on the identified categorical variable, which will create stratums(subset), based on the categories.
We can understand with better example. We have 100 observation in a dataset. In this dataset i select a categorical variable “Gender”. Now when i divide the population using this Gender, 70 fall under female and 30 under Male. Now i need a subset of 10 observation, for which 7 will be selected out from 70 and 3 will be selected out from 30. From stratum we select sample, using “Simple Random Sampling” .
In Simple Words, Population is divided into Stratum( Subsets) based on some common categories using stratified sampling, then sample will be selected from the subsets using simple Random Sampling. 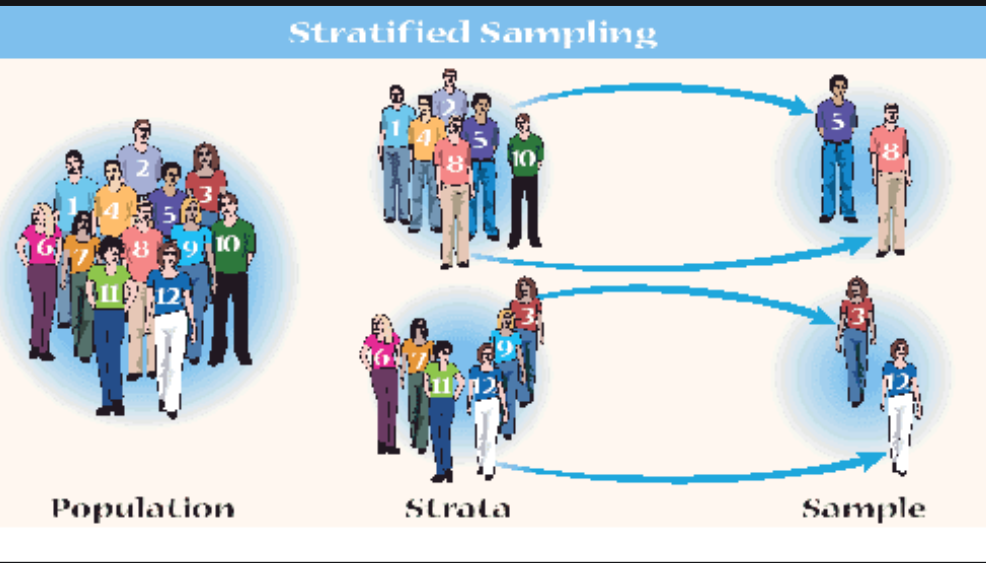
Below picture explains all in one..