Here we are going to see the feature selection for numerical values with R implementation.
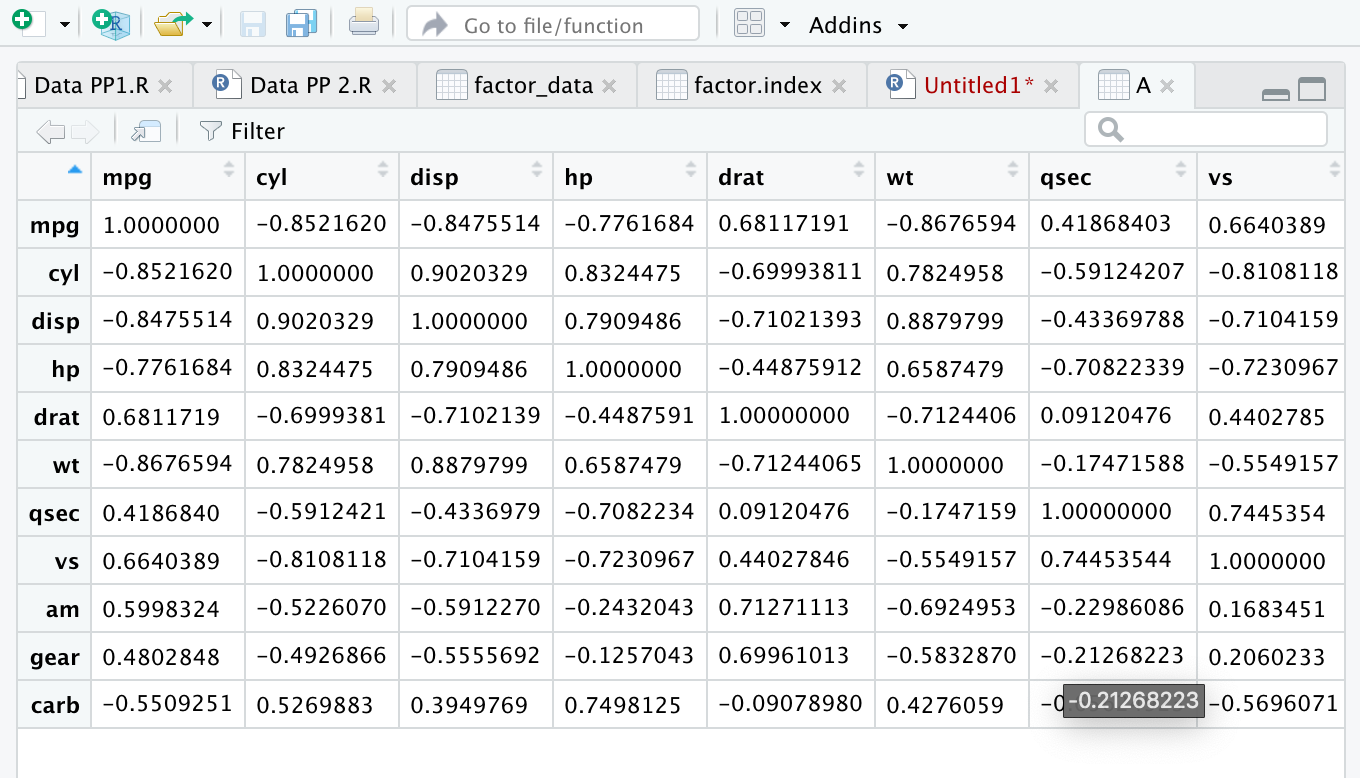
- For numerical values - We apply correlation analysis ## Correlation Analysis - R Implementation install.packages(“corrplot”) // Install respective pkg A = cor(mtcars) // cor function to calculate correlation View(A)
Methods for plotting corr graph
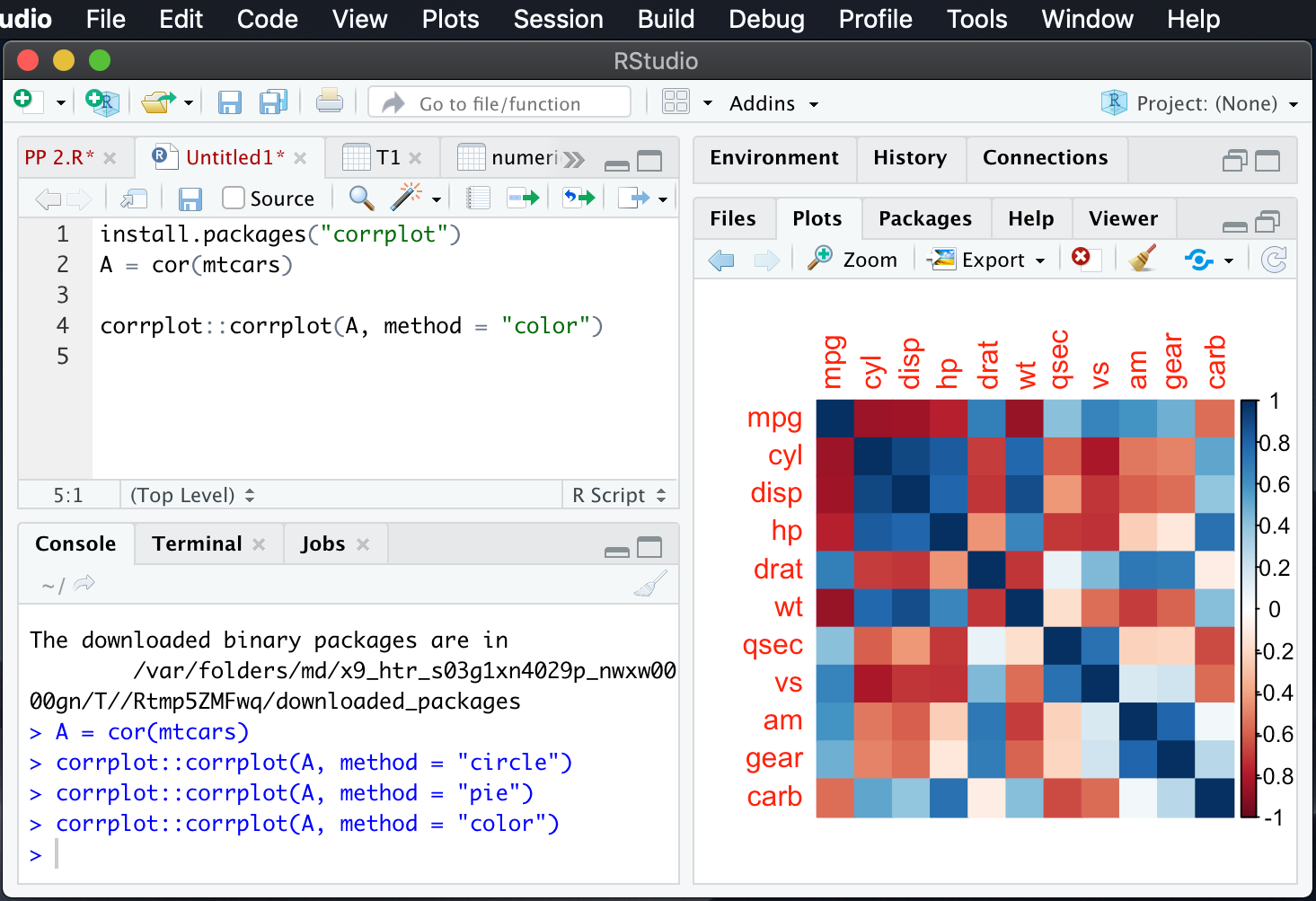
Note:- Dark Blue indicates- Highly positively correlated
Dark Red indicates - Highly negatively correlated
corrplot::corrplot(A, method = “circle”)
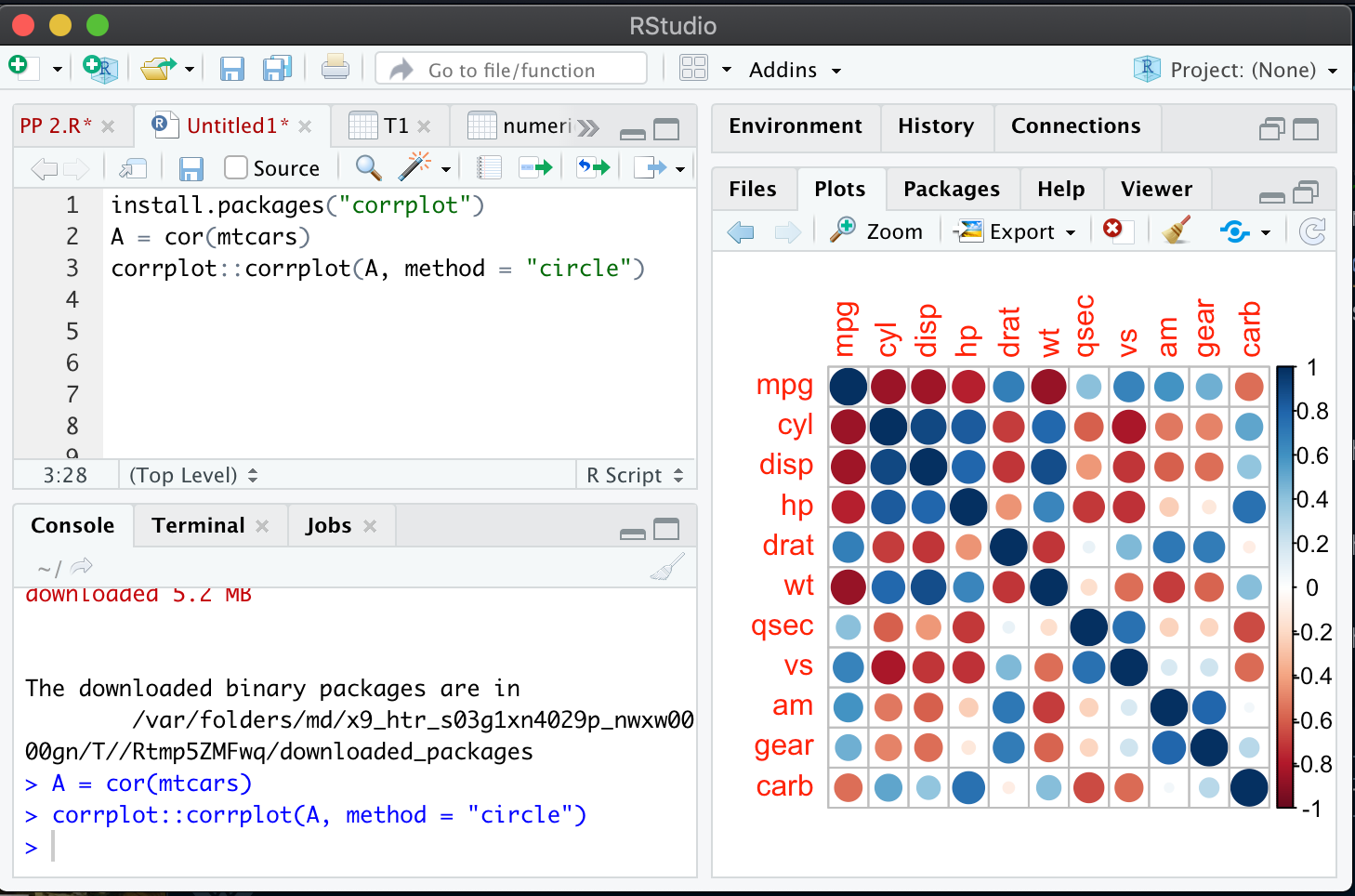
In the above pic, mpg and cyl is highly negatively correlated and mpg and VS are highly positively correlated. In this way we have to understand.
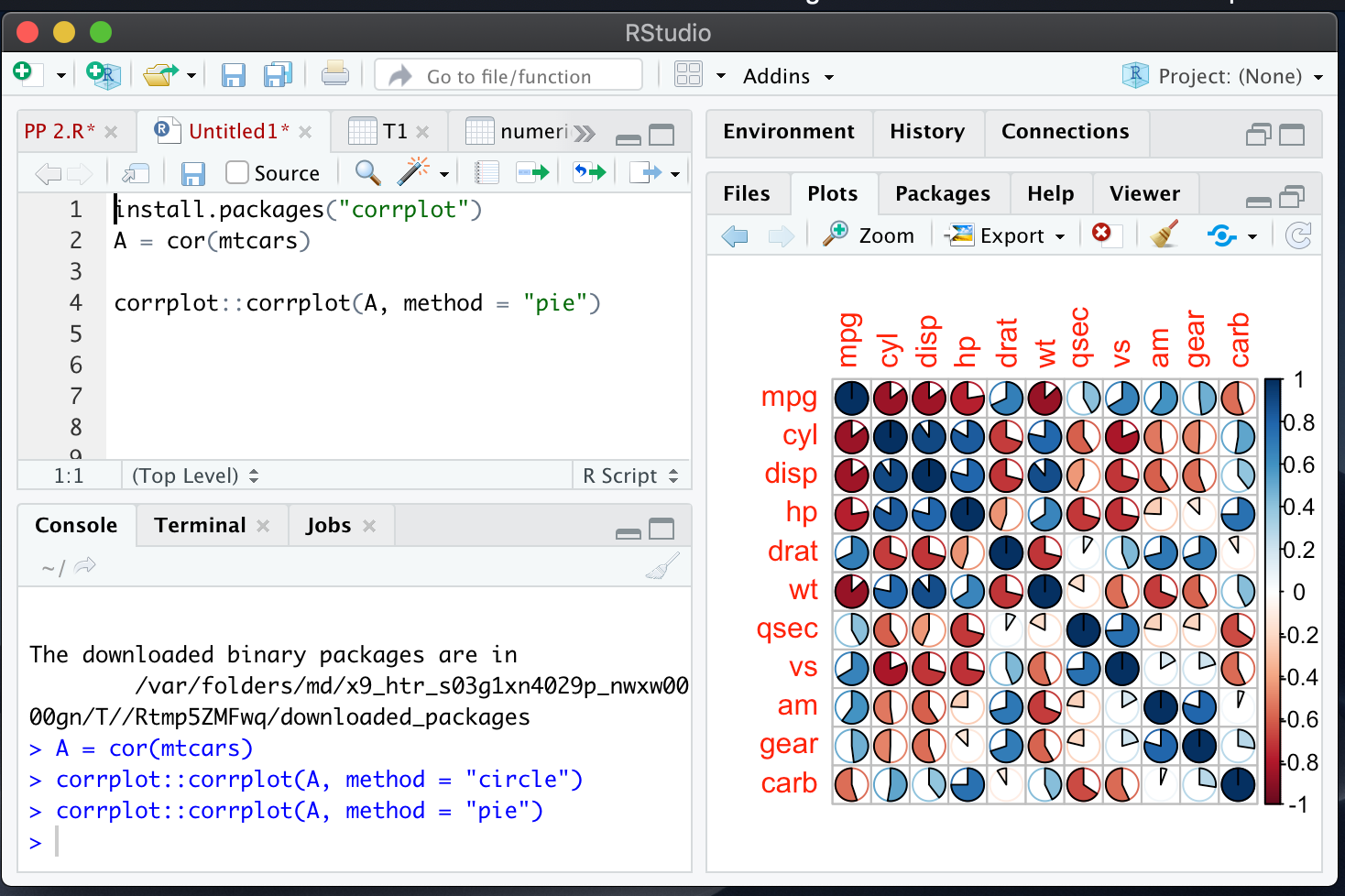
corrplot::corrplot(A, method = “pie”)
 corrplot::corrplot(A, method = “color”)
corrplot::corrplot(A, method = “color”)
Above is for mtcars dataset which has all values in numeric. Now let us take one dataset which has both numeric and categorical values see below picture.. in below commands, we filter only numerical values and draw corr graph, see the fifth command. 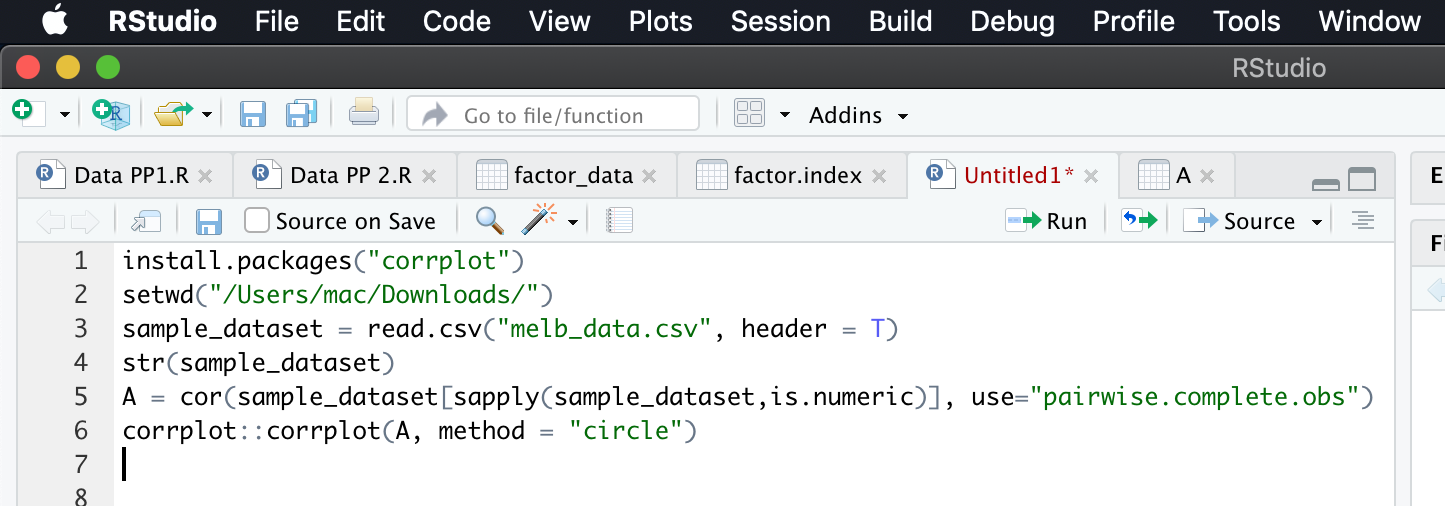
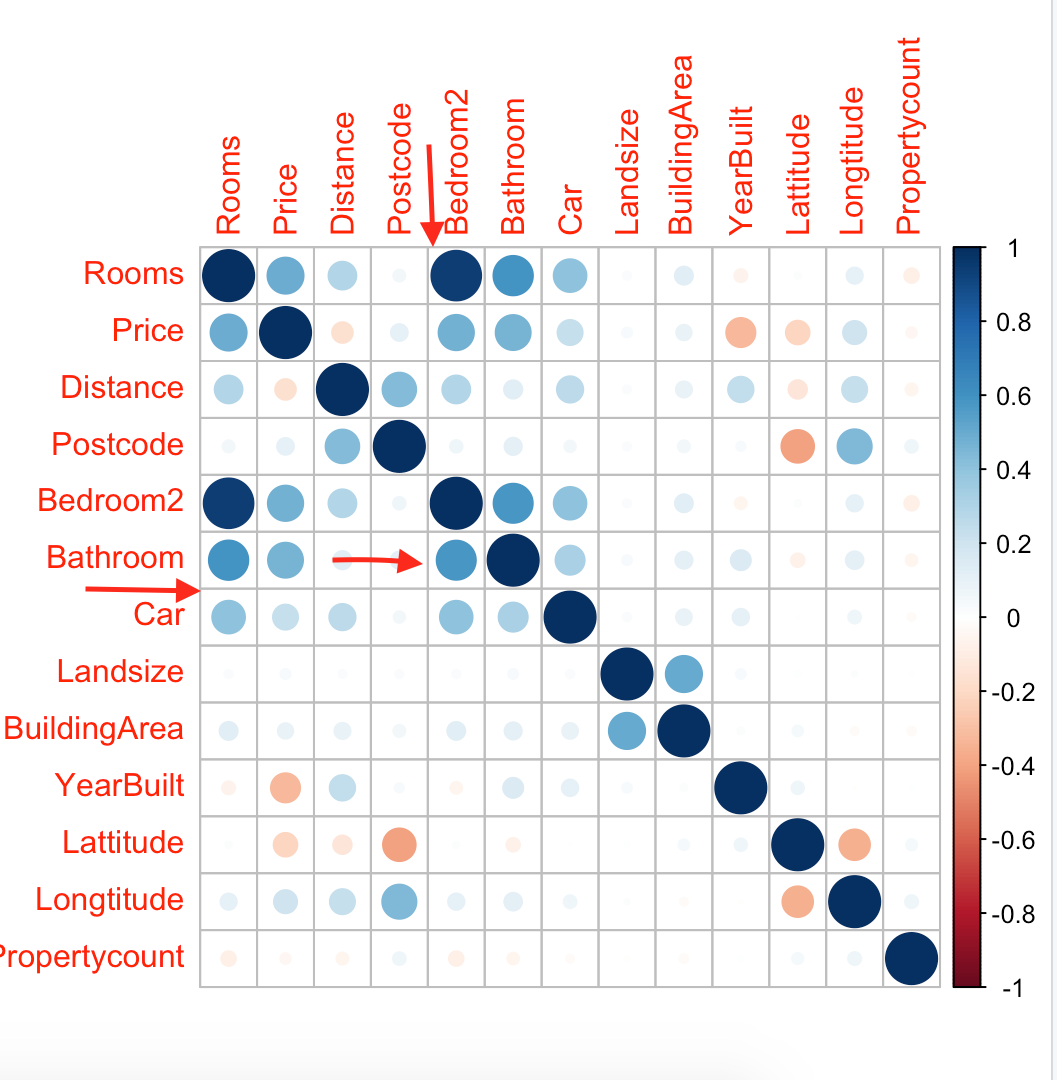 In above picture, see the rooms row and bedroom2 column, which is in dark blue, (means highly positively correlated). So we can ignore any one. Let us ignore bedroom2. So here is the variable list to ignore.
In above picture, see the rooms row and bedroom2 column, which is in dark blue, (means highly positively correlated). So we can ignore any one. Let us ignore bedroom2. So here is the variable list to ignore.
- Bedroom2
- Bathroom
- Building Area
The rule is:
The independent variables should be highly negatively correlated. If two variables are highly positively correlated, then we should take either one. Feeding both ,which are having same info, will increase the complexity of the ML Model. So..
Note:- Independent variables should be negatively correlated within themselves.
Every single Independent Variable should be positively correlated with dependent(Target) variable.
With this we will end up this, up next will be about Chi Square Analysis. Happy blogging!!!